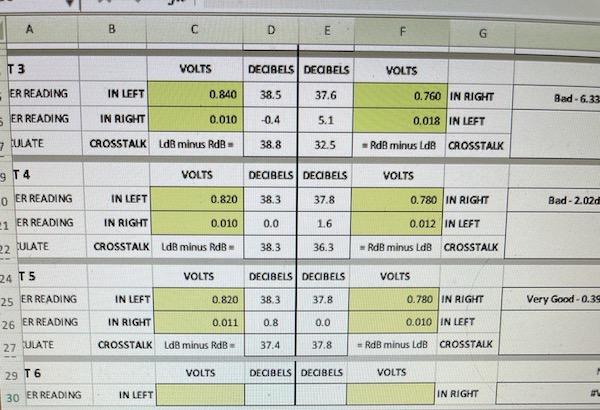
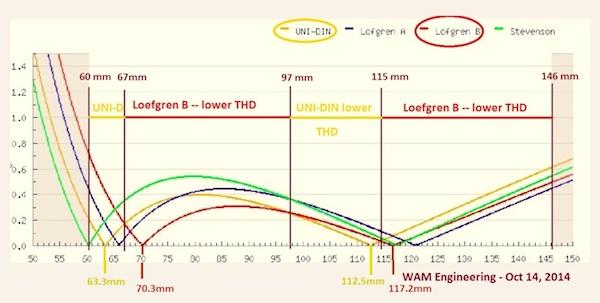
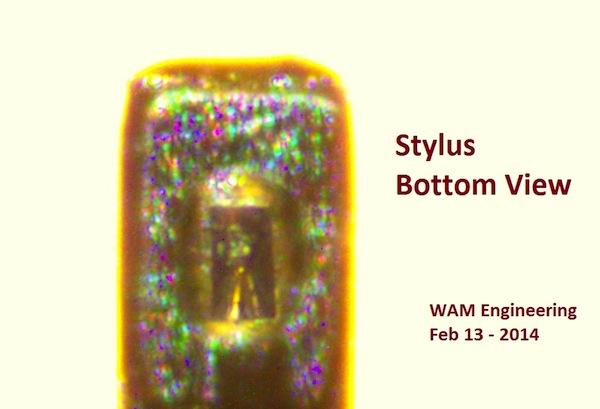
|
Mar 03, 2022
|
Mar 19, 2021
|
Aug 11, 2020
|
Aug 02, 2020
|
Apr 21, 2020
|
Oct 23, 2017
|
Aug 21, 2013
|
Feb 19, 2014